Find a Decodable Book User Guide
Preface
This guide is intended for authorized users of Lexile Find a Decodable Book who access and use the tool for classroom purposes. This document provides an overview and step-by-step guidance on how to access and use the tool.
Lexile Find a Decodable Book Description
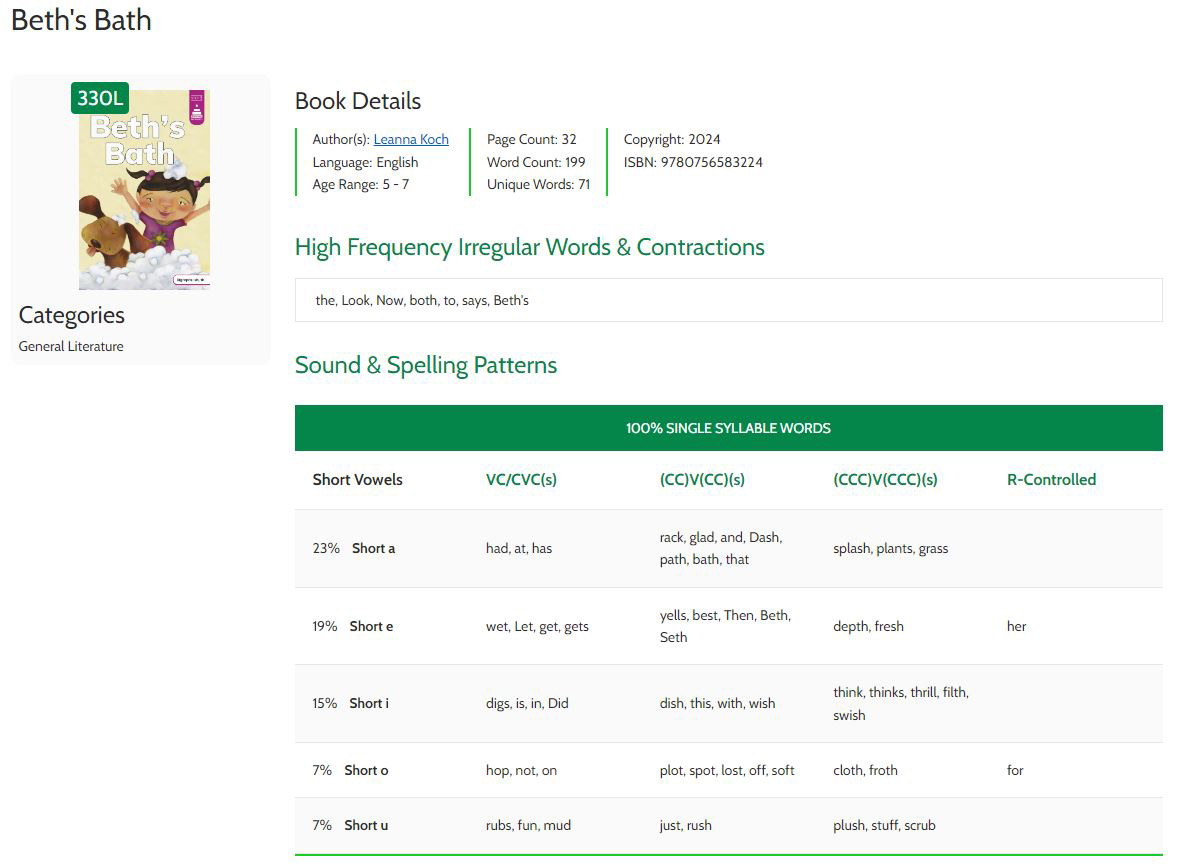
Lexile Find a Decodable Book tool is designed to help educators find books that support phonics-based instruction. Users can select a specific vowel sound to discover published decodable books that include the selected sound. Results can be sorted by Lexile measure, percentage match of the vowel sound, and number of words in the book. The book details page includes a decodability analysis of the words in the book, including various vowel sounds, high-frequency irregular words, and contractions.
Features and Functionality
Lexile Find a Decodable Book Features
With the Lexile Find a Decodable Book tool users can:
- Search published decodable books
- Filter book search by vowel sound
- View book details including spelling patterns, sound patterns, irregular words, and contractions
Premium Lexile and Quantile Hub membership includes access to advanced features across all the Lexile and Quantile tools. Educators in Lexile and Quantile partner states are automatically enrolled in premium membership to the Lexile and Quantile Hub. To take advantage of this special opportunity, educators should register using their school- or district-issued email address. Visit membership options to learn more.
How It Works
Overview
Lexile Find a Decodable Book allows users to filter decodable texts based on vowel patterns and sounds. Once selected, additional book details provide educators targeted information to design phonics-based instruction for students.
Step 1: Locate the tool
- Select the Tools Menu
- Select Find a Decodable Book tool
Remember! Whenever you are logging into your Hub account it is important to use your school email address.
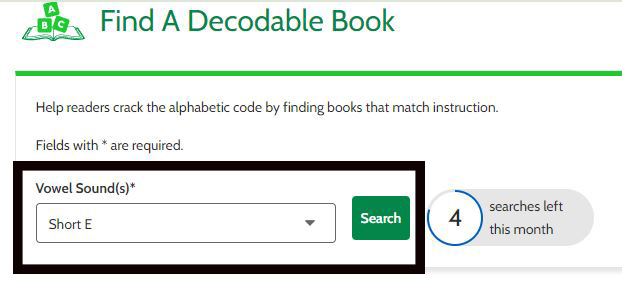
Step 2: Select a Vowel Sound
- Use the drop-down menu to filter your search by vowel sound.
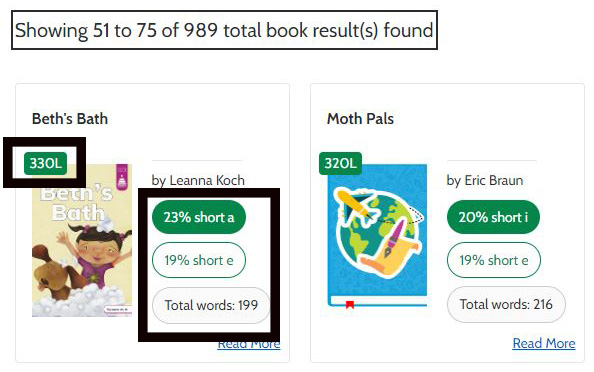
Step 3: View Book Results
- The results page includes decodable texts that include a high percentage of words with the selected vowel sound.
- Results also indicate what other vowel sounds are included in the decodable book and the total words
- The Lexile text measure is also included to help you match texts with your students. first image
- Book results can be sorted based on percentage match, Lexile measure, and word count. Just select from the menu on the results page. (Second image - Image is used for demonstration only and does not represent actual book results).
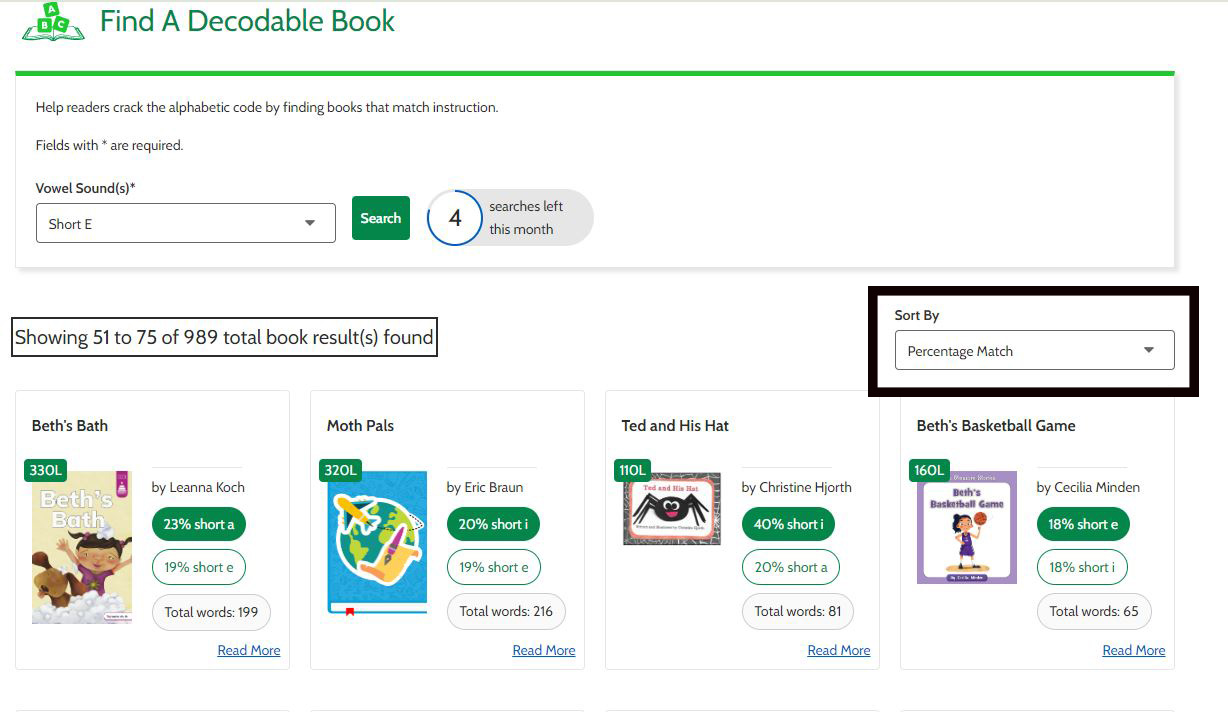
Step 4: Read More About the Book
- Select the Read More link to view additional information about the book.
- You may also select “Purchase Book” if you wish to buy this book.
- Once you have finished reviewing these book details, select the Back to Results button to return to your previous results page.
Classroom Application
Tailor Reading Materials to Meet the Needs of Your Students
Sort books by vowel sound and examine the difficulty of reading material based on high-frequency irregular words, Lexile text measure, and text length. Knowing the Lexile text measure of a reading material helps educators determine what types of support may be needed for students during instruction.
Pre Teach Vocabulary
View the vocabulary words that have been identified as consequential in the text from your analysis. Determine which words might be challenging for students and pre teach them to set your students up for success.
Design phonics-based instructional groups
Use this tool to help your students crack the alphabetic code by finding books that match your phonics-based instruction. The Lexile Find a Decodable Book tool allows you to quickly find a decodable text that will meet the diverse needs of your early readers.
Most Frequently Asked Questions
|
How are the High Frequency Irregular Words determined? |
High Frequency Irregular Words include:
|
|
What do the different short vowel categories in the decodability analysis mean? |
VC/CVC(s): This column is for words with short vowel sounds and a spelling pattern of:
|
(CC)V(CC)(s): This column is for words with short vowel sounds and a spelling pattern of:
|
|
(CCC)V(CCC)(s): This column is for words with short vowel sounds and a spelling pattern of:
|
|
R Controlled: This column is for words with short vowel sounds and a spelling pattern of:
|
|
What do the different long vowel categories in the decodability analysis mean? |
V/CV: This column is for words with long vowel sounds and a spelling pattern of:
|
(CC)VCe(s): This column is for words with long vowel sounds and a spelling pattern of:
|
|
Vowel Teams: This column is for words with long vowel sounds and a spelling pattern of two vowels next to each other, including:
|
